Let’s start with
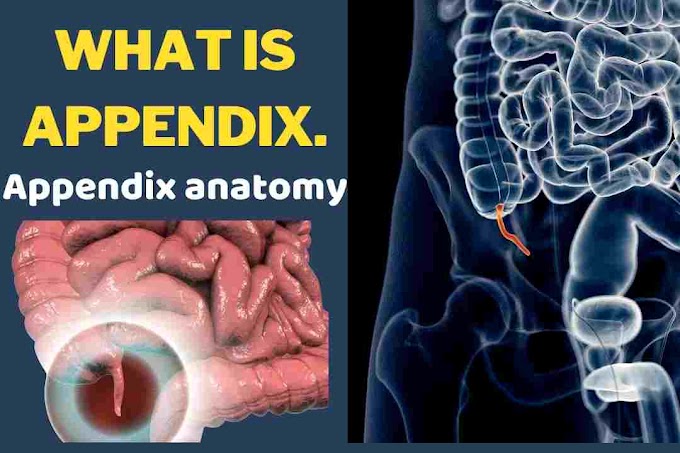
anatomy the appendix
I located at the inferior cecum and is about four to twelve centimeters long. The arterial supply is the appendiceal artery which is a branch of the ileocolic artery. The Appendix can be located in a retrocecal position in about two-thirds of people appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix.
The most common
symptoms of appendicitis are pain initially around the umbilicus, then it can
migrate to the right lower quadrant to McBurney's point which is one-third of
the way between the anterior superior iliac spine and the umbilicus. the pain precedes nausea patients usually
don't want to eat so if you ask a kid if they want a hamburger and they say no
that is sometimes called the hamburger sign always ask about diarrhea which can
occur with appendicitis but could also be due to infectious colitis, Which can
sometimes also present with right lower quadrant pain such as in Yersinia
infections. sometimes children will
have large inflamed lymph nodes in the bowel mesentery called mesenteric
adenitis, that can mimic appendicitis and needs no treatment the other named
signs of appendicitis include Rovsing's sign, which is a pain in the right
lower quadrant with palpation of the left lower quadrant. Right lower quadrant
pain with coughing called Dunphy sign and pain with extension or internal
rotation of the right leg known as the psoas sign. The Alvarado score takes all
of these factors along with some lab findings to grade the likelihood of
appendicitis a ruptured appendix and a right inguinal hernia is called an
Amyand hernia.
if an appendix is causing pain and then
ruptures the patient can feel better for a short while then gradually get sick
again. The most common location for rupture is the anti-mesenteric appendix
about halfway down as the blood supply is the worst here. The differential diagnosis for right lower
quadrant pain in a woman is the mnemonic. ROPE appendicitis ruptured ovarian
cyst ovarian torsion PID endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy. So also consider pelvic ultrasound and
always do a pregnancy test in a woman of childbearing age. Appendicitis is
diagnosed on ultrasound as a thick-walled over two millimeters thick dilated
over seven-millimeter non-compressible structure in the right lower
quadrant. The most sensitive and
specific test is a ct scan.
Classic symptoms
in a male may not need any imaging, although I think at least an ultrasound is
not a bad idea because I've been fooled by terminal ileal Crohn's disease in the past appendectomy is
generally still considered the best treatment for non-ruptured. Or recently
ruptured appendicitis laparoscopic or open through McBurney's incision muscle
splitting in the right lower quadrant.
if it's a ruptured appendix and you do a good abdominal washout only
continue the post-operative antibiotics for four days as per the STOP-IT trial
non-operative treatment with antibiotics alone.
as studied in the landmark CODA which stands for comparison of outcomes
of antibiotic drugs and appendectomy trial can be considered in some early
appendicitis although 30 percent still
needed surgery within a few months also know that a fecalith or an
appendicolith which are calcified stool balls in the base of the appendix. immunosuppression and peritoneal signs should
be considered contraindications to trying non-operative treatment of acute
appendicitis.
I would also consider appendectomy more in the
elderly population or if there was any evidence of a mass on imaging. Since
cancer is more of a concern a pregnant woman's evaluation should start with an ultrasound
but the appendix can be hard to find so they can also have a non-contrast MRI
which is good imaging for appendicitis.
Ruptured appendicitis is a risk for a fetal loss so be careful in
pregnant patients not to miss appendicitis because of the gravid uterus. The
appendix can be near the right upper quadrant sometimes a supraumbilical Hassan
trocar is safer and all ports should be in the upper abdomen to stay away from
the uterus. if you explore for right lower quadrant pain and the appendix is normal
check for terminal ileum Crohn's disease also check for Meckel's Diverticulum
which should be within two feet of the ileocecal valve and check for GYN causes
in a woman if you find terminal ilium Crohn's disease that does not involve the
cecum then remove the appendix.
if your Crohn's disease involves the base of
the appendix. but the appendix is normal then leave the appendix since removal
has a high rate of fistula if there is a drainable abscess and the patient is
otherwise stable IR drainage and
antibiotics is best don't do surgery right away if there is a phlegmon without
a drainable abscess just antibiotics and no immediate surgery also if you treat
a ruptured appendix that has an abscess or a phlegmon non-operatively you will
need to decide if you will offer an interval appendectomy usually in about six
weeks this is a divided issue. a safe answer is that anybody with imaging six
weeks later showing a mass in the appendix should have it removed to rule out
cancer older patients may want it removed also to rule out cancer and certainly
anybody over the age of 40 should at least have a barium enema or a colonoscopy
to be sure the appendicitis is not related to malignancy. The trend is away
from routine interval appendectomy in everybody certainly appendiceal cancer is
a common question the appendix is one location you can find neuroendocrine or
carcinoid tumors.
the most common
location for carcinoids in the ileum but the appendix is the second most common
location if an appendiceal carcinoid tumor is less than two centimeters and is
at the tip of the appendix then appendectomy alone is sufficient appendiceal
carcinoid over two centimeters at the tip of the appendix needs a right
hemicolectomy. if appendiceal carcinoid of any size is at the base of the
appendix then you need a right hemicolectomy.
Any
adenocarcinoma of the appendix no matter what size gets a right hemicolectomy
adenocarcinoma tumors of the appendix get a right hemicolectomy and
adenocarcinoma of the terminal ileum gets a right hemicolectomy a Mucocele is a
dilated appendix filled with mucin .these are not all malignant but should be
treated as possibly malignant until they have removed the general term now is
appendiceal mucinous neoplasm or AMN and they range from low grade to high
grade the following decision tree is generally recommended if a Mucocele is
found on imaging strongly consider a colonoscopy to look at the cecum and the
base of the appendix for tumor if there is no obvious tumor and colonoscopy
prepare for an appendectomy but consent the patient for a possible right
hemicolectomy appendectomy can be done laparoscopically but you must be careful
not to rupture the appendix if you can't remove adhesions without risk of
rupture then do the appendectomy open.
if the appendix is ruptured even
low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms
can cause diffuse mucin throughout the
abdomen this is known as pseudomyxoma
peritonei or pmp if possible take a
little cecum with the appendix especially if the base of the appendix is also dilated with
mucin once you remove the appendix if
you can you should send it for frozen
section if it is benign or a low grade
appendiceal mucinous neoplasm which has
not penetrated the muscularis propria
and if the margins are negative and if the
appendix is not dilated to more than
two centimeters then you can stop after
appendectomy alone but any higher grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm or mucinous adenocarcinoma or if the
appendix is dilated to more than two
centimeters then you should do a right
hemicolectomy if somebody gets
pseudomyxoma peritonei then the patient
should be referred for debulking and
heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy or HIPEC
Typhlitis is inflammation of the cecum related to neutropenia the classic presentation is
a neutropenic patient with right lower
quadrant pain and dilated inflamed
cecum on the ct scan you have to
operate.
if they are
septic or free air, but most Typhlitis
is treated with iv antibiotics and bowel rest patients with HIV can also get CMV colitis of the right colon
with Hemorrhagic ulcerated lesions of the mucosa. The pathognomonic finding is
owl-eyed nuclear inclusions in colonocytes on endoscopic biopsy intussusception
is common at the ileocecal valve, In children, it is commonly due to benign
enlarged lymph nodes. So trying air contrast enema to reduce it and don't
operate in adults, however there is usually a
lead point that is malignant or will lead to recurrent episodes, so take
ileocecal intussusception in adults to the or for resection Ogilvie's syndrome
is also known as colonic pseudo-obstruction classic presentation is an elderly
patient with electrolyte abnormalities or recent back surgery or
retroperitoneal inflammation of some sort it is thought to be caused by too much
sympathetic tone.
the cecum will be dilated typically
about 8 to 10 centimeters and a patient
will have right lower quadrant pain and
bloating initial treatment is ng tube
bowel rest and correcting any
underlying electrolyte problems and
minimizing narcotics i would try and do
a gentle gastrographin enema to rule out
distal obstruction if no distal obstruction
and conservative measures are not working try two milligrams of iv neostigmine which
increases parasympathetics and should
make the colon contract and the patient
have a big bowel movement it can cause bradycardia though so have atropine half a milligram up to a
milligram iv ready to counteract this
atropine will block the parasympathetic
action on the heart don't use neostigmine
if a patient has heart block neostigmine
can be repeated but probably only try
it twice before moving on colonoscopic
decompression is an option if
neostigmine doesn't work although
minimal insufflation is used failure of these dilation over 12 centimeters peritoneal signs or free air would be indications to operate for right colon resection and
likely an ileostomy and a mucous fistula
at that point Cecal volvulus occurs in younger patients than sigmoid volvulus and is due to
abnormal attachments of the right colon
Cecal volvulus is not treated with
decompressive endoscopy .
it requires surgery the most safe surgery is a right hemicholectomy simple cecopexy is associated with high recurrence risk cecal bascule is when the cecum folds up and
over on itself probably resection is the
best to treat this since it is common
in younger women and you want to
decrease future recurrence right side
colon diverticula is unusual but it is
more commonly found in asian populations
sometimes actual diverticulitis of the cecum and or right colon can occur this usually
responds to conservative measures but
once resolving you definitely need to do
a colonoscopy to rule out cancer
occasionally an AVM also known as
angiodysplasia of the right colon can
be a source of gi bleed a tagged rbc scan can pick up bleeding of 0.5 cc's per minute or
more an angiogram needs bleeding of 1 cc per minute or more if bleeding scans show blush in the right
colon try an angiogram and embolization colonoscopy with injection or cautery may also work
if neither of these work and the
bleeding continues then do a right
hemicolectomy or a subtotal colectomy if
the source is unclear that's it for
appendix and cecum there will be a separate talk on the rest of the colon. If you like this
information, kindly shares it with other peoples.
If you have any
question, kindly comment below in this article, I will reply as soon as
possible



0 Comments
Please donot enter any spam link in comment box!